1.定义概览
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的单源最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
2.实例演示
设结点1为起点,依次求到其它结点的最短路径。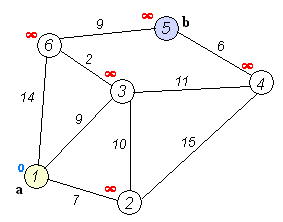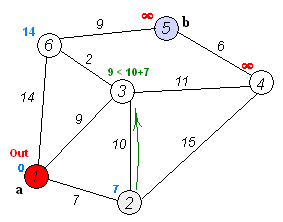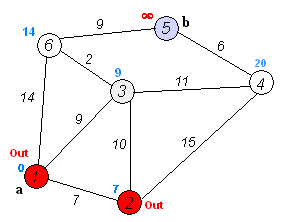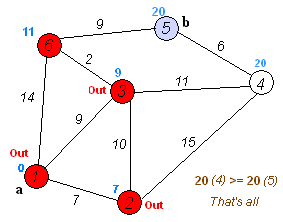
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法求最短路径
* @author sunbufu
*
*/
public class ShortestPathDijkstra {
/**无穷大*/
final static int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] points = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int[][] weights = {
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
{0, 7, 9, INF, INF, 14 },//1
{7, 0, 10, 15, INF, INF },//2
{9, 10, 0, 11, INF, 2 },//3
{INF, 15, 11, 0, 6, INF },//4
{INF, INF, INF, 6, 0, 9 },//5
{14, INF, 2, INF, 9, 0 } //6
};
dijkstra(points, weights);
}
public static void dijkstra(int[] points, int[][] weights) {
int pointsNumber = points.length;
boolean[] finsih = new boolean[pointsNumber];// 是否已经确定该点的最短路径
int[] shortestPathWeights = new int[pointsNumber];// 最短路径的权值
int[] previousPoint = new int[pointsNumber];// 路径中,该结点的上一个结点
// 初始化
for (int i = 1; i < pointsNumber; i++) {
shortestPathWeights[i] = weights[0][i];
finsih[i] = false;
if (shortestPathWeights[i] == INF)// 如果跟起点没有直接关联
previousPoint[i] = -1;// 上一结点置为无效
else
previousPoint[i] = 0;// 否则上一结点置为起点
}
finsih[0] = true;
// 计算距离起点的最短路径
for (int i = 1; i < pointsNumber; i++) {
int shortestPath = INF;
int point = 0;// 当前未被最终确定的节点中,离起点最近的
for (int j = 0; j < pointsNumber; j++) {// 寻找距离起点最近的顶点
if (!finsih[j] && shortestPathWeights[j] < shortestPath) {// 没有被最终确定,并且该距离小于上一个
shortestPath = shortestPathWeights[j];
point = j;
}
}
finsih[point] = true;
// 计算跟其余已知最短路径的,修正最短路径
for (int j = 0; j < pointsNumber; j++) {
if (!finsih[j] && weights[point][j] < INF) {
if (shortestPathWeights[point] + weights[point][j] < shortestPathWeights[j]) {// 如果通过point,更新距离起点更短的路径
shortestPathWeights[j] = shortestPathWeights[point] + weights[point][j];
previousPoint[j] = point;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < pointsNumber; i++) {
System.out.println(points[i] + "\t最短路径的权值 = " + shortestPathWeights[i] + ",\t上一个结点 = " + previousPoint[i]);
}
}
}
3.总结
迪杰斯特拉算法解决了从一个结点到各个结点的最短路径问题,时间复杂度为O(n^2)